Use ordered pairs where the \(x\)-values represent the age and the \(y\)-values represent the corresponding value. If the results of calculating the basis were graphed, it would appear as a straight line, hence the name. The straight-line basis is the simplest way to determine the loss of value of an asset over time.
Revision in Estimates of Useful life and Residual Value
Compared to the other three methods, straight line depreciation is by far the simplest. According to straight-line depreciation, this is how much depreciation you have to subtract from the value of an asset each year to know its book value. Book value refers to the total value of an asset, taking into account how much it’s depreciated up to the current point in time.
- Shopping for small business accounting software can be painful and confusing.
- The estimates of useful life or residual value of an asset may need to be revised in subsequent accounting periods in order to reflect more accurately the pattern of economic benefits in light of new information.
- To limit the rental cost to \($66\), the truck can be driven \(40\) miles or less.
- Book value refers to the total value of an asset, taking into account how much it’s depreciated up to the current point in time.
- Use this data to construct a linear function that models the value of the piece of equipment over time.
Understanding Linear Depreciation: Definition, Calculation, and Application
This https://x.com/BooksTimeInc may not be true for all assets, in which case a different method should be used. Unlike more complex methodologies, such as double declining balance, this method uses only three variables to calculate the amount of depreciation each accounting period. Companies use depreciation for physical assets, and amortization for intangible assets such as patents and software. Note that part of the depreciation rate formula’s appeal is its simplicity, though a simple equation might not offer an accurate picture.
Download the Straight Line Depreciation Template
- Suppose an asset for a business cost $11,000, will have a life of 5 years and a salvage value of $1,000.
- Accountants use the straight line depreciation method because it is the easiest to compute and can be applied to all long-term assets.
- It is one of the simplest and most commonly used depreciation methods in accounting and finance.
- One of the most obvious pitfalls of using this method is that the useful life calculation is often based on guesswork.
- The first section explains straight-line, sum-of-years’ digits, declining-balance, and double-declining-balance depreciation.
As a beginner, it is possible to harbor misconceptions about depreciation. For example, some believe that depreciation is a form of provision https://www.bookstime.com/bookkeeping-services/minneapolis for the repair or replacement of assets, which is incorrect. It makes it possible to correctly assess the cost of investments for the company. This is because the useful life of an asset does not represent how long it continues to function, but rather how long it is useful for business purposes. The cost of a daily truck rental is \($48.00\), plus an additional \($0.45\) for every mile driven. Write a function that gives the cost of the daily truck rental and use it to determine the total cost of renting the truck for a day and driving it \(60\) miles.

Salary & Income Tax Calculators

Many accountants use a simple, easy-to-use method called the straight-line basis. This method spreads out the depreciation equally over each accounting period. To calculate depreciation using a straight-line basis, simply divide the net price (purchase price less linear depreciation function the salvage price) by the number of useful years of life the asset has.
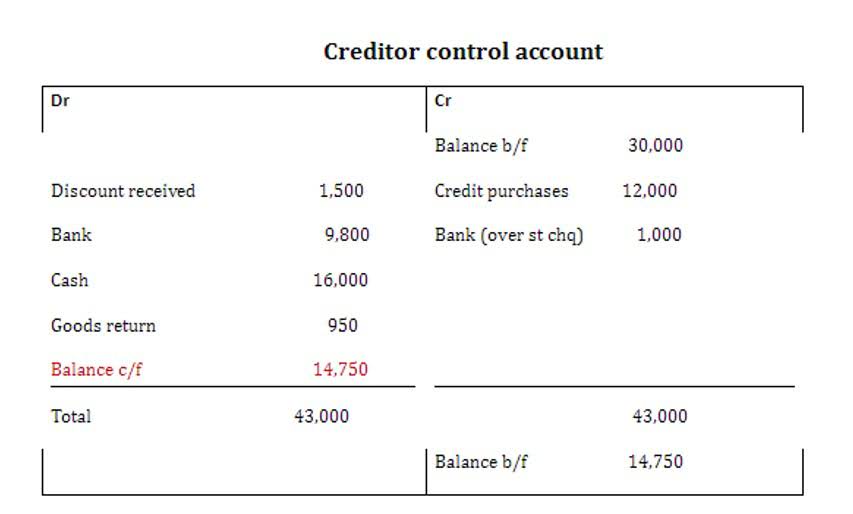

The straight-line method of depreciation assumes a constant rate of depreciation. It calculates how much a specific asset depreciates in one year, and then depreciates the asset by that amount every year after that. Our exploration would not be complete without addressing the impact of depreciation on a company’s costs and profitability.